- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anti-quorum sensing potential of selenium nanoparticles against LasI/R, RhlI/R, and PQS/MvfR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a molecular docking approach
Read this article at
Abstract
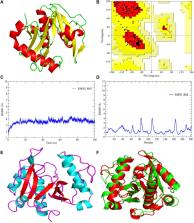
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an infectious pathogen which has the ability to cause primary and secondary contagions in the blood, lungs, and other body parts of immunosuppressed individuals, as well as community-acquired diseases, such as folliculitis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, and others. This opportunistic bacterium displays drug resistance and regulates its pathogenicity via the quorum sensing (QS) mechanism, which includes the LasI/R, RhlI/R, and PQS/MvfR systems. Targeting the QS systems might be an excellent way to treat P. aeruginosa infections. Although a wide array of antibiotics, namely, newer penicillins, cephalosporins, and combination drugs are being used, the use of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) to cure P. aeruginosa infections is extremely rare as their mechanistic interactions are weakly understood, which results in carrying out this study. The present study demonstrates a computational approach of binding the interaction pattern between SeNPs and the QS signaling proteins in P. aeruginosa, utilizing multiple bioinformatics approaches. The computational investigation revealed that SeNPs were acutely ‘locked’ into the active region of the relevant proteins by the abundant residues in their surroundings. The PatchDock-based molecular docking analysis evidently indicated the strong and significant interaction between SeNPs and the catalytic cleft of LasI synthase (Phe105-Se = 2.7 Å and Thr121-Se = 3.8 Å), RhlI synthase (Leu102-Se = 3.7 Å and Val138-Se = 3.2 Å), transcriptional receptor protein LasR (Lys42-Se = 3.9 Å, Arg122-Se = 3.2 Å, and Glu124-Se = 3.9 Å), RhlR (Tyr43-Se = 2.9 Å, Tyr45-Se = 3.4 Å, and His61-Se = 3.5 Å), and MvfR (Leu208-Se = 3.2 Å and Arg209-Se = 4.0 Å). The production of acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) was inhibited by the use of SeNPs, thereby preventing QS as well. Obstructing the binding affinity of transcriptional regulatory proteins may cause the suppression of LasR, RhlR, and MvfR systems to become inactive, thereby blocking the activation of QS-regulated virulence factors along with their associated gene expression. Our findings clearly showed that SeNPs have anti-QS properties against the established QS systems of P. aeruginosa, which strongly advocated that SeNPs might be a potent solution to tackle drug resistance and a viable alternative to conventional antibiotics along with being helpful in therapeutic development to cure P. aeruginosa infections.
Related collections
Most cited references96
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found