- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Evaluation of the composition and in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of Cilantro ( Coriandrum sativum L. leaves) cultivated in Saudi Arabia (Al-Kharj)
Abstract
Background
In the present study, we explored the composition of Cilantro ( Coriandrum sativum L. leaves) essential oil (CEO) cultivated in Saudi Arabia (Al-Kharj) and explored its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory effects in vitro.
Methods
Gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy was used to detect the CEO composition. The 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH)-induced free radical and ferric chloride scavenging methods were used to determine the antioxidant activity. Antimicrobial activity was investigated using the well diffusion method. Anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated using egg albumin and trypsin-induced inflammation methods.
Results
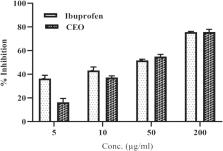
Forty-six compounds representing 90.17% of the total aroma were identified in the CEO; the major constituents were found to be 1-decanol (17.85%), decanal (11.04%), trans-2-dodecen-1-ol (7.87%), menthone (6.71%), 2-decen-1-ol, trans- (5.44%), dodecanal (4.76%), trans-tetradec-2-enal (3.14%), sedanolide (3.02), and thymol (3.01%). DPPH-induced free radical and ferric chloride scavenging assays demonstrated low antioxidant effects of CEO, and the antioxidant activity was observed at a high CEO concentration. The antimicrobial activity of CEO was assessed against 5 microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) by using well diffusion methods; CEO was found to possess excellent antimicrobial activity against all microorganisms, except Escherichia coli. Moreover, CEO demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory activity against egg albumin- and trypsin-induced inflammation.
Related collections
Most cited references36

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: a current perspective
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found