- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Revitalizing brain perfusion: Unveiling advancements through rhythm control strategies in atrial fibrillation—A systematic review
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Recent evidence suggests an elevated risk of cognitive impairment and dementia in individuals with atrial fibrillation (AF), irrespective of stroke occurrence. AF, known to reduce brain perfusion, particularly through silent cerebral ischemia, underscores the intricate relationship between cardiac and cerebral health. The heart plays a crucial role in supporting normal brain function, and rhythm control, a standard AF treatment, has demonstrated enhancements in brain perfusion. This systematic review aimed to examine published data concerning the influence of rhythm control on brain perfusion in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Methods
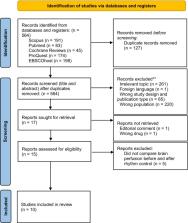
A systematic search for relevant studies was carried out in Scopus, PubMed, Cochrane Reviews, ProQuest, and EBSCOhost, spanning from their inception until April 30, 2023. Studies that specifically examined brain perfusion following any form of rhythm control in atrial fibrillation were included in the review.
Results
The review encompassed 10 studies involving 436 participants. Among these, six utilized electrical cardioversion for rhythm control. The majority (8 out of 10) demonstrated that restoring sinus rhythm markedly enhances brain perfusion. In one of the two remaining studies, notable improvement was observed specifically in a region closely linked to cognition. Additionally, both studies reporting data on the Mini‐Mental State Examination (MMSE) showed a consistent and significant increase in scores following rhythm control.
Abstract
This study examines rhythm control's impact on brain perfusion in atrial fibrillation, filling a research gap as there are no systematic reviews on this topic. Analyzing 10 studies with 436 participants, we find a positive association between rhythm control in AF patients and enhanced brain blood flow, improving cognitive function.
Related collections
Most cited references44

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham Heart Study: a cohort study
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
