- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MXene in the lens of biomedical engineering: synthesis, applications and future outlook
Read this article at
Abstract
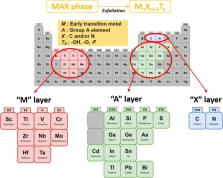
MXene is a recently emerged multifaceted two-dimensional (2D) material that is made up of surface-modified carbide, providing its flexibility and variable composition. They consist of layers of early transition metals (M), interleaved with n layers of carbon or nitrogen (denoted as X) and terminated with surface functional groups (denoted as T x/T z) with a general formula of M n+1X nT x, where n = 1–3. In general, MXenes possess an exclusive combination of properties, which include, high electrical conductivity, good mechanical stability, and excellent optical properties. MXenes also exhibit good biological properties, with high surface area for drug loading/delivery, good hydrophilicity for biocompatibility, and other electronic-related properties for computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Due to the attractive physicochemical and biocompatibility properties, the novel 2D materials have enticed an uprising research interest for application in biomedicine and biotechnology. Although some potential applications of MXenes in biomedicine have been explored recently, the types of MXene applied in the perspective of biomedical engineering and biomedicine are limited to a few, titanium carbide and tantalum carbide families of MXenes. This review paper aims to provide an overview of the structural organization of MXenes, different top-down and bottom-up approaches for synthesis of MXenes, whether they are fluorine-based or fluorine-free etching methods to produce biocompatible MXenes. MXenes can be further modified to enhance the biodegradability and reduce the cytotoxicity of the material for biosensing, cancer theranostics, drug delivery and bio-imaging applications. The antimicrobial activity of MXene and the mechanism of MXenes in damaging the cell membrane were also discussed. Some challenges for in vivo applications, pitfalls, and future outlooks for the deployment of MXene in biomedical devices were demystified. Overall, this review puts into perspective the current advancements and prospects of MXenes in realizing this 2D nanomaterial as a versatile biological tool.
Related collections
Most cited references112

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ror2 signaling regulates Golgi structure and transport through IFT20 for tumor invasiveness
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3 AlC2.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found