- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Reducing stillbirths: interventions during labour
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Approximately one million stillbirths occur annually during labour; most of these stillbirths occur in low and middle-income countries and are associated with absent, inadequate, or delayed obstetric care. The low proportion of intrapartum stillbirths in high-income countries suggests that intrapartum stillbirths are largely preventable with quality intrapartum care, including prompt recognition and management of intrapartum complications. The evidence for impact of intrapartum interventions on stillbirth and perinatal mortality outcomes has not yet been systematically examined.
Methods
We undertook a systematic review of the published literature, searching PubMed and the Cochrane Library, of trials and reviews (N = 230) that reported stillbirth or perinatal mortality outcomes for eight interventions delivered during labour. Where eligible randomised controlled trials had been published after the most recent Cochrane review on any given intervention, we incorporated these new trial findings into a new meta-analysis with the Cochrane included studies.
Results
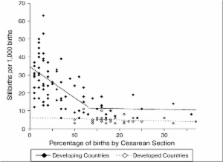
We found a paucity of studies reporting statistically significant evidence of impact on perinatal mortality, especially on stillbirths. Available evidence suggests that operative delivery, especially Caesarean section, contributes to decreased stillbirth rates. Induction of labour rather than expectant management in post-term pregnancies showed strong evidence of impact, though there was not enough evidence to suggest superior safety for the fetus of any given drug or drugs for induction of labour. Planned Caesarean section for term breech presentation has been shown in a large randomised trial to reduce stillbirths, but the feasibility and consequences of implementing this intervention routinely in low-/middle-income countries add caveats to recommending its use. Magnesium sulphate for pre-eclampsia and eclampsia is effective in preventing eclamptic seizures, but studies have not demonstrated impact on perinatal mortality. There was limited evidence of impact for maternal hyperoxygenation, and concerns remain about maternal safety. Transcervical amnioinfusion for meconium staining appears promising for low/middle income-country application according to the findings of many small studies, but a large randomised trial of the intervention had no significant impact on perinatal mortality, suggesting that further studies are needed.
Conclusion
Although the global appeal to prioritise access to emergency obstetric care, especially vacuum extraction and Caesarean section, rests largely on observational and population-based data, these interventions are clearly life-saving in many cases of fetal compromise. Safe, comprehensive essential and emergency obstetric care is particularly needed, and can make the greatest impact on stillbirth rates, in low-resource settings. Other advanced interventions such as amnioinfusion and hyperoxygenation may reduce perinatal mortality, but concerns about safety and effectiveness require further study before they can be routinely included in programs.
Related collections
Most cited references155
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
No cry at birth: global estimates of intrapartum stillbirths and intrapartum-related neonatal deaths.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found