- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing
Read this article at
Abstract
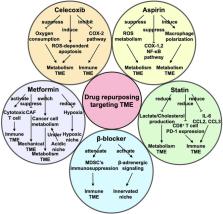
Accumulating evidence shows that cellular and acellular components in tumor microenvironment (TME) can reprogram tumor initiation, growth, invasion, metastasis, and response to therapies. Cancer research and treatment have switched from a cancer-centric model to a TME-centric one, considering the increasing significance of TME in cancer biology. Nonetheless, the clinical efficacy of therapeutic strategies targeting TME, especially the specific cells or pathways of TME, remains unsatisfactory. Classifying the chemopathological characteristics of TME and crosstalk among one another can greatly benefit further studies exploring effective treating methods. Herein, we present an updated image of TME with emphasis on hypoxic niche, immune microenvironment, metabolism microenvironment, acidic niche, innervated niche, and mechanical microenvironment. We then summarize conventional drugs including aspirin, celecoxib, β-adrenergic antagonist, metformin, and statin in new antitumor application. These drugs are considered as viable candidates for combination therapy due to their antitumor activity and extensive use in clinical practice. We also provide our outlook on directions and potential applications of TME theory. This review depicts a comprehensive and vivid landscape of TME from biology to treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references168

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type–specific intracellular bacteria
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found