- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mechanisms of Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Stiffening in Mice Revealed by a Functional Genetics Assay of Structural, Functional, and Transcriptomic Data
Read this article at
Abstract
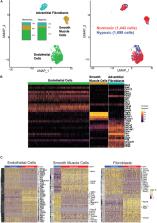
Hypoxia adversely affects the pulmonary circulation of mammals, including vasoconstriction leading to elevated pulmonary arterial pressures. The clinical importance of changes in the structure and function of the large, elastic pulmonary arteries is gaining increased attention, particularly regarding impact in multiple chronic cardiopulmonary conditions. We establish a multi-disciplinary workflow to understand better transcriptional, microstructural, and functional changes of the pulmonary artery in response to sustained hypoxia and how these changes inter-relate. We exposed adult male C57BL/6J mice to normoxic or hypoxic (FiO 2 10%) conditions. Excised pulmonary arteries were profiled transcriptionally using single cell RNA sequencing, imaged with multiphoton microscopy to determine microstructural features under in vivo relevant multiaxial loading, and phenotyped biomechanically to quantify associated changes in material stiffness and vasoactive capacity. Pulmonary arteries of hypoxic mice exhibited an increased material stiffness that was likely due to collagen remodeling rather than excessive deposition (fibrosis), a change in smooth muscle cell phenotype reflected by decreased contractility and altered orientation aligning these cells in the same direction as the remodeled collagen fibers, endothelial proliferation likely representing endothelial-to-mesenchymal transitioning, and a network of cell-type specific transcriptomic changes that drove these changes. These many changes resulted in a system-level increase in pulmonary arterial pulse wave velocity, which may drive a positive feedback loop exacerbating all changes. These findings demonstrate the power of a multi-scale genetic-functional assay. They also highlight the need for systems-level analyses to determine which of the many changes are clinically significant and may be potential therapeutic targets.
Related collections
Most cited references89
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found