- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
MiR-223-3p promotes cell proliferation and metastasis by downregulating SLC4A4 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Read this article at
Abstract
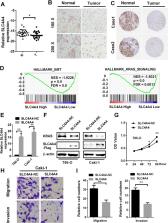
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known to affect the occurrence and progression of cancer. We therefore evaluated the involvement of miR-223-3p in renal cell cancer. MiR-223-3p was highly expressed in clear cell renal cell cancer tissues. Clear cell renal cell cancer patients with higher miR-223-3p expression had higher tumor stages and grades and poorer prognoses. In renal cancer cells, overexpression of miR-223-3p enhanced cell proliferation and metastasis, while inhibition of miR-223-3p reduced the malignant capacity of the cells. MiR-223-3p was found to bind directly to solute carrier family 4, member 4 ( SLC4A4) mRNA, thereby reducing SLC4A4 mRNA and protein expression. SLC4A4 overexpression restrained cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS) expression in renal cancer cells. SLC4A4 expression correlated negatively with miR-223-3p expression in patient samples. Given that miR-223-3p suppressed the SLC4A4/KRAS axis, miR-223-3p gene therapy could be an effective treatment for renal cancer.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The SLC transporter in nutrient and metabolic sensing, regulation, and drug development
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found