- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dust-bathing behavior of laying hens in enriched colony housing systems and an aviary system
Read this article at
Abstract
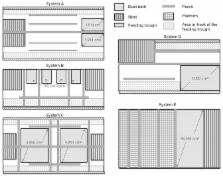
The dust-bathing behavior of Lohmann Selected Leghorn hens was compared in 4 enriched colony housing systems and in an aviary system. The enriched colony housing systems differed especially in the alignment and division of the functional areas dust bath, nest, and perches. Forty-eight-hour video recordings were performed at 3 time-points during the laying period, and focal animal sampling and behavior sampling methods were used to analyze the dust-bathing behavior. Focal animal data included the relative fractions of dust-bathing hens overall, of hens bathing in the dust-bath area, and of those bathing on the wire floor throughout the day. Behavior data included the number of dust-bathing bouts within a predefined time range, the duration of 1 bout, the number of and reasons for interruptions, and the number of and reasons for the termination of dust-bathing bouts. Results showed that the average duration of dust bathing varied between the 4 enriched colony housing systems compared with the aviary system. The duration of dust-bathing bouts was shorter than reported under natural conditions. A positive correlation between dust-bathing activity and size of the dust-bath area was observed. Frequently, dust baths were interrupted and terminated by disturbing influences such as pecking by other hens. This was especially observed in the enriched colony housing systems. In none of the observed systems, neither in the enriched colony housing nor in the aviary system, were all of the observed dust baths terminated “normally.” Dust bathing behavior on the wire mesh rather than in the provided dust-bath area generally was observed at different frequencies in all enriched colony housing systems during all observation periods, but never in the aviary system. The size and design of the dust-bath area influenced the prevalence of dust-bathing behavior in that small and subdivided dust-bath areas reduced the number of dust-bathing bouts but increased the incidence of sham dust bathing on the wire mesh.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The stress of not being able to perform dustbathing in laying hens.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Dustbathing behavior of laying hens as related to quality of dustbathing material
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found