- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Yellow nail syndrome: a review
Read this article at
Abstract
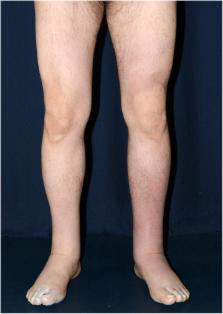
Yellow nail syndrome (YNS; OMIM 153300, ORPHA662) is a very rare disorder that almost always occurs after 50 years of age but a juvenile or familial form has also been observed. YNS is diagnosed based on a triad associating yellow nail discoloration, pulmonary manifestations (chronic cough, bronchiectasia, pleural effusion) and lower limb lymphedema. Chronic sinusitis is frequently associated with the triad. YNS etiology remains unknown but a role of lymphatic impairment is usually evoked. YNS is more frequently isolated but may be associated in rare cases with autoimmune diseases, other clinical manifestations implicating lymphatic functions or cancer and, hence, is also considered a paraneoplastic syndrome. YNS management is symptomatic and not codified. YNS can resolve spontaneously. Oral vitamin E alone or even better when associated with triazole antifungals may achieve partial or total disappearance of nail discoloration. Pleural effusion can be treated surgically, with decortication/pleurectomy or pleurodesis. Antibiotic prophylaxis is prescribed for bronchiectasia with chronic sputum production. Lymphedema treatment is based on low-stretch bandages and the wearing of elastic compression garments combined with skin care, exercises and, as needed, manual lymph drainage.
Related collections
Most cited references132
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Risk factors for erysipelas of the leg (cellulitis): case-control study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A systematic review of the evidence for complete decongestive therapy in the treatment of lymphedema from 2004 to 2011.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found