- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reviving tourism industry post-COVID-19: A resilience-based framework
Read this article at
Abstract
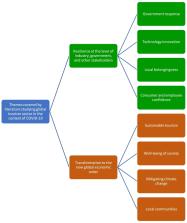
The COVID-19 pandemic struck the tourism industry severely. Based on the review of 35 papers that studied the tourism industry in the wake of the pandemic, we propose a resilience-based framework for reviving the global tourism industry post-COVID-19. Our framework outlines four prominent factors for building resilience in the industry: government response, technology innovation, local belongingness, and consumer and employee confidence. We argue that using such inclusive resilience; the tourism industry may transform into a new global economic order characterized by sustainable tourism, society's well-being, climate action, and the involvement of local communities. We also offer directions for future research in the area.
Highlights
Related collections
Most cited references71
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pandemics, tourism and global change: a rapid assessment of COVID-19
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
