- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Crisis management research (1985–2020) in the hospitality and tourism industry: A review and research agenda
Read this article at
Abstract
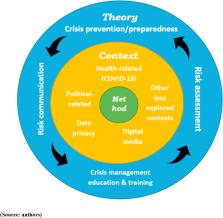
The global tourism industry has already suffered an enormous loss due to COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) in 2020. Crisis management, including disaster management and risk management, has been becoming a hot topic for organisations in the hospitality and tourism industry. This study aims to investigate relevant research domains in the hospitality and tourism industry context. To understand how crisis management practices have been adopted in the industry, the authors reviewed 512 articles including 79 papers on COVID-19, spanning 36 years, between 1985 and 2020. The findings showed that the research focus of crisis management, crisis impact and recovery, as well as risk management, risk perception and disaster management dominated mainstream crisis management research. Look back the past decade (2010 to present), health-related crisis (including COVID-19), social media, political disturbances and terrorism themes are the biggest trends. This paper proposed a new conceptual framework for future research agenda of crisis management in the hospitality and tourism industry. Besides, ten possible further research areas were also suggested in a TCM (theory-context-method) model: the theories of crisis prevention and preparedness, risk communication, crisis management education and training, risk assessment, and crisis events in the contexts of COVID-19, data privacy in hospitality and tourism, political-related crisis events, digital media, and alternative analytical methods and approaches. In addition, specific research questions in these future research areas were also presented in this paper.
Related collections
Most cited references627
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
