- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mutant p53 partners in crime
Read this article at
Abstract
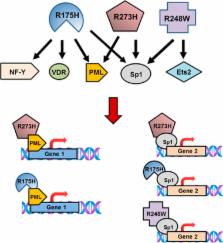
Mutant p53 proteins impart changes in cellular behavior and function through interactions with proteins that alter gene expression. The milieu of intracellular proteins available to interact with mutant p53 is context specific and changes with disease, cell type, and environmental conditions. Varying conformations of mutant p53 largely dictate protein–protein interactions as different point mutations within protein-coding regions greatly alter the extent and array of gain-of-function (GOF) activities. Given such variables, how can knowledge regarding p53 missense mutations be translated into predicting or altering biologic activity for therapy? How may knowledge regarding mutant p53 functions within certain disease contexts be harnessed to blunt or ablate mutant p53 GOF for therapy? In this article, we review known proteins that interact with mutant p53 and result in the activation of genes that contribute to p53 GOF with particular emphasis on context dependency and an evolving appreciation of GOF mechanisms.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mutant p53: one name, many proteins.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mutant p53 gain of function in two mouse models of Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found