- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Association between fatty liver disease and hearing impairment in Korean adults: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
We hypothesized that fatty liver disease (FLD) is associated with a high prevalence of hearing loss (HL) owing to metabolic disturbances. This study aimed to evaluate the association between FLD and HL in a large sample of the Korean population.
Methods
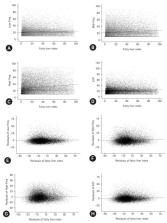
We used a dataset of adults who underwent routine voluntary health checkups (n=21,316). Fatty liver index (FLI) was calculated using Bedogni’s equation. The patients were divided into two groups: the non-FLD (NFLD) group (n=18,518, FLI <60) and the FLD group (n=2,798, FLI ≥60). Hearing thresholds were measured using an automatic audiometer. The average hearing threshold (AHT) was calculated as the pure-tone average at four frequencies (0.5, 1, 2, and 3 kHz). HL was defined as an AHT of >40 dB.
Results
HL was observed in 1,370 (7.4%) and 238 patients (8.5%) in the NFLD and FLD groups, respectively ( p=0.041). Compared with the NFLD group, the odds ratio for HL in the FLD group was 1.16 ( p=0.040) and 1.46 ( p<0.001) in univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses, respectively. Linear regression analyses revealed that FLI was positively associated with AHT in both univariate and multivariate analyses. Analyses using a propensity score-matched cohort showed trends similar to those using the total cohort.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A new definition for metabolic associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Global Epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in Patients with type 2 diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found