- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
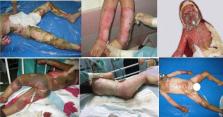
Pan drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing nosocomial infections among burnt children
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: Nosocomial infection caused by Acinetobacter baumannii has emerged as a world-wide serious problem in the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR). Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant strains of A. baumannii cannot be completely eliminated among the infected patients. This study aimed to monitor antibiotic resistance among A. baumannii strains isolated from burnt children.
Methods: After performing biochemical identification tests on 115 isolates, 62 were detected as A. baumannii . Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was used to test susceptibility to colistin, and disk agar diffusion was used for the susceptibility of the isolates to the antibiotics Ciprofloxacin, Amikacin, Gentamicin, Cefepime, Meropenem, Imipenem, Ceftazidime, Levofloxacin and Piperacillin/Tazobactam. Bacterial species were isolated and identified as multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR) and pan drug-resistant (PDR), based on the susceptibility patterns to elected antibiotics, deputing different classes of antimicrobial.
Results: The antibiotic susceptibility pattern out of a total of 62 bacterial strains used in this study. Thirty-six (58%) strains were categorized as MDR, 17 (27.5%) as XDR, and nine (14.5%) as PDR.
Conclusion: To reduce the threat of antimicrobial resistance, MDR, XDR and PDR A. baumannii strains must be evaluated by all clinical microbiology laboratories.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Acinetobacter baumannii: epidemiology, antimicrobial resistance, and treatment options.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found