- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Natural History of Tuberculosis: Duration and Fatality of Untreated Pulmonary Tuberculosis in HIV Negative Patients: A Systematic Review
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The prognosis, specifically the case fatality and duration, of untreated tuberculosis is important as many patients are not correctly diagnosed and therefore receive inadequate or no treatment. Furthermore, duration and case fatality of tuberculosis are key parameters in interpreting epidemiological data.
Methodology and Principal Findings
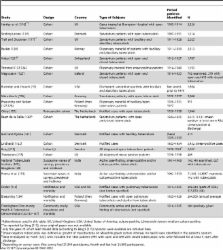
To estimate the duration and case fatality of untreated pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV negative patients we reviewed studies from the pre-chemotherapy era. Untreated smear-positive tuberculosis among HIV negative individuals has a 10-year case fatality variously reported between 53% and 86%, with a weighted mean of 70%. Ten-year case fatality of culture-positive smear-negative tuberculosis was nowhere reported directly but can be indirectly estimated to be approximately 20%. The duration of tuberculosis from onset to cure or death is approximately 3 years and appears to be similar for smear-positive and smear-negative tuberculosis.
Conclusions
Current models of untreated tuberculosis that assume a total duration of 2 years until self-cure or death underestimate the duration of disease by about one year, but their case fatality estimates of 70% for smear-positive and 20% for culture-positive smear-negative tuberculosis appear to be satisfactory.
Related collections
Most cited references201
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The competitive cost of antibiotic resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
HIV infection and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: the perfect storm.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found