- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interspecies Interactions Between Streptococcus Mutans and Streptococcus Agalactiae in vitro
Read this article at
Abstract
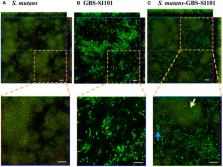
Streptococcus mutans is an oral species closely associated with dental caries. As an early oral colonizer, S. mutans utilizes interspecies coaggregation to promote the colonization of subsequent species and affect polymicrobial pathogenesis. Previous studies have confirmed several adhering partner species of S. mutans, including Candida albicans and Fusobacterium nucleatum. In this study, we discovered new intergeneric co-adherence between S. mutans and the saliva isolate Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS-SI101). Research shows that GBS typically colonizes the human gastrointestinal and vaginal tracts. It is responsible for adverse pregnancy outcomes and life-threatening infections in neonates and immunocompromised people. Our results revealed that GtfB and GtfC of S. mutans, which contributed to extracellular polysaccharide synthesis, promoted coaggregation of S. mutans with GBS-SI101. In addition, oral streptococci, including Streptococcus sanguinis, Streptococcus gordonii and S. mutans, barely inhibited the growth of GBS-SI101. This study indicated that S. mutans could help GBS integrate into the Streptococcus-associated oral polymicrobial community and become a resident species in the oral cavity, increasing the risk of oral infections.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell-cell distance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Bacteriocins: evolution, ecology, and application.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found