- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Modified hyaluronic acid hydrogels with chemical groups that facilitate adhesion to host tissues enhance cartilage regeneration
Read this article at
Abstract
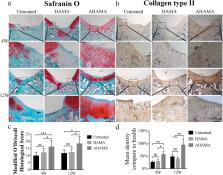
Stable integration of hydrogel implants with host tissues is of critical importance to cartilage tissue engineering. Designing and fabricating hydrogels with high adhesive strength, stability and regeneration potential are major challenges to be overcome. This study fabricated injectable adhesive hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogel modified by aldehyde groups and methacrylate (AHAMA) on the polysaccharide backbone with multiple anchoring mechanisms (amide bond through the dynamic Schiff base reaction, hydrogen bond and physical interpenetration). AHAMA hydrogel exhibited significantly improved durability and stability within a humid environment (at least 7 days), together with higher adhesive strength (43 KPa to skin and 52 KPa to glass), as compared to commercial fibrin glue (nearly 10 KPa) and HAMA hydrogel (nearly 20 KPa). The results showed that AHAMA hydrogel was biocompatible and could be easily and rapidly prepared in situ. In vitro cell culture experiments showed that AHAMA hydrogel could enhance proliferation (1.2-folds after 3 days) and migration (1.5-folds after 12 h) of bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs), as compared to cells cultured in a culture dish. Furthermore, in a rat osteochondral defect model, implanted AHAMA hydrogel significantly promoted integration between neo-cartilage and host tissues, and significantly improved cartilage regeneration (modified O'Driscoll histological scores of 16.0 ± 4.1 and 18.3 ± 4.6 after 4 and 12-weeks of post-implantation in AHAMA groups respectively, 12.0 ± 2.7 and 12.2 ± 2.8 respectively in HAMA groups, 9.8 ± 2.4 and 11.5 ± 2.1 respectively in untreated groups). Hence, AHAMA hydrogel is a promising adhesive biomaterial for clinical cartilage regeneration and other biomedical applications.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Adhesive hydrogel composed of single natural polymer component.
-
•
The single component enhance stable and easy to use in surgical operation of hydrogel.
-
•
Adhesive hydrogel exhibited strong adhesive strength through multiple anchoring mechanisms.
-
•
Adhesive hydrogel promoted integration between neo-cartilage and host tissues, drastically improved cartilage regeneration.
Related collections
Most cited references58
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The chemistry and engineering of polymeric hydrogel adhesives for wound closure: a tutorial.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
