- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Review on Antiulcer Activity of Few Indian Medicinal Plants
Read this article at
Abstract
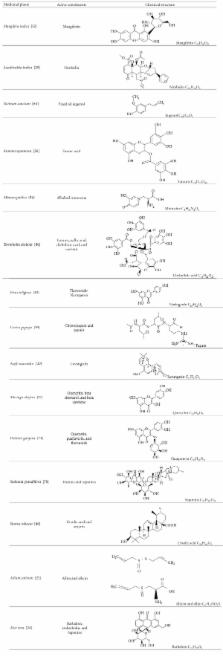
Ulcer is a common gastrointestinal disorder which is seen among many people. It is basically an inflamed break in the skin or the mucus membrane lining the alimentary tract. Ulceration occurs when there is a disturbance of the normal equilibrium caused by either enhanced aggression or diminished mucosal resistance. It may be due to the regular usage of drugs, irregular food habits, stress, and so forth. Peptic ulcers are a broad term that includes ulcers of digestive tract in the stomach or the duodenum. The formation of peptic ulcers depends on the presence of acid and peptic activity in gastric juice plus a breakdown in mucosal defenses. A number of synthetic drugs are available to treat ulcers. But these drugs are expensive and are likely to produce more side effects when compared to herbal medicines. The literature revealed that many medicinal plants and polyherbal formulations are used for the treatment of ulcer by various ayurvedic doctors and traditional medicinal practitioners. The ideal aims of treatment of peptic ulcer disease are to relieve pain, heal the ulcer, and delay ulcer recurrence. In this review attempts have been made to know about some medicinal plants which may be used in ayurvedic as well as modern science for the treatment or prevention of peptic ulcer.
Related collections
Most cited references53
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Systematic Review of the Epidemiology of Complicated Peptic Ulcer Disease: Incidence, Recurrence, Risk Factors and Mortality
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found