- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Recent Breakthroughs in the Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Morella and Myrica Species
Read this article at
Abstract
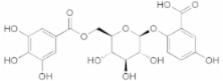
Oxidative stress is one of the risk factors for the development of several chronic diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants are therefore highly sought and can be seen as a type of preventive medicine against several diseases. Myrica and Morella genus (Myricaceae) are taxonomically very close and their species are trees or shrubs with edible fruits that exhibit relevant uses in traditional medicine, for instance in Chinese or Japanese folk medicine they are used to treat diarrhea, digestive problems, headache, burns and skin diseases. Nearly 36 compounds were isolated from different morphological parts of Myrica and/or Morella species and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities evaluated. Thirteen of these compounds exhibit greater effects than the positive controls used. Adenodimerin A was the most active compound reported (in a 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assay EC 50= 7.9 ± 0.3 µM). These results are just one aspect of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory evaluations reported regarding Myrica and Morella species, so a comprehensive overview on the current status, highlighting the antioxidant health promoting effect of these species, their key antioxidant compounds as well as the compounds with protective effects against oxidative stress related diseases such as inflammation, is relevant.
Related collections
Most cited references88

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Oxidative Stress, Prooxidants, and Antioxidants: The Interplay
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of flavonoids.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found