- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interactions of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Polymicrobial Wound Infection
Read this article at
Abstract
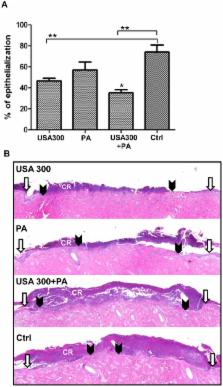
Understanding the pathology resulting from Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa polymicrobial wound infections is of great importance due to their ubiquitous nature, increasing prevalence, growing resistance to antimicrobial agents, and ability to delay healing. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus USA300 is the leading cause of community-associated bacterial infections resulting in increased morbidity and mortality. We utilized a well-established porcine partial thickness wound healing model to study the synergistic effects of USA300 and P. aeruginosa on wound healing. Wound re-epithelialization was significantly delayed by mixed-species biofilms through suppression of keratinocyte growth factor 1. Pseudomonas showed an inhibitory effect on USA300 growth in vitro while both species co-existed in cutaneous wounds in vivo. Polymicrobial wound infection in the presence of P. aeruginosa resulted in induced expression of USA300 virulence factors Panton-Valentine leukocidin and α-hemolysin. These results provide evidence for the interaction of bacterial species within mixed-species biofilms in vivo and for the first time, the contribution of virulence factors to the severity of polymicrobial wound infections.