- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications
Read this article at
Abstract

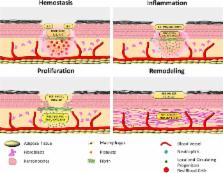
The chronic nature and associated complications of nonhealing wounds have led to the emergence of nanotechnology-based therapies that aim at facilitating the healing process and ultimately repairing the injured tissue. A number of engineered nanotechnologies have been proposed demonstrating unique properties and multiple functions that address specific problems associated with wound repair mechanisms. In this outlook, we highlight the most recently developed nanotechnology-based therapeutic agents and assess the viability and efficacy of each treatment, with emphasis on chronic cutaneous wounds. Herein we explore the unmet needs and future directions of current technologies, while discussing promising strategies that can advance the wound-healing field.
Abstract
A myriad of advanced nanotechnology-driven therapies were designed for targeting specific problems of chronic wound healing. The clinical application of these therapies still requires intensive research for the standardization of nanotechnologies.
Related collections
Most cited references114
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Bacterial Biofilms: A Common Cause of Persistent Infections
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
