- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Short-chain fatty acids as modulators of redox signaling in health and disease
Read this article at
Abstract
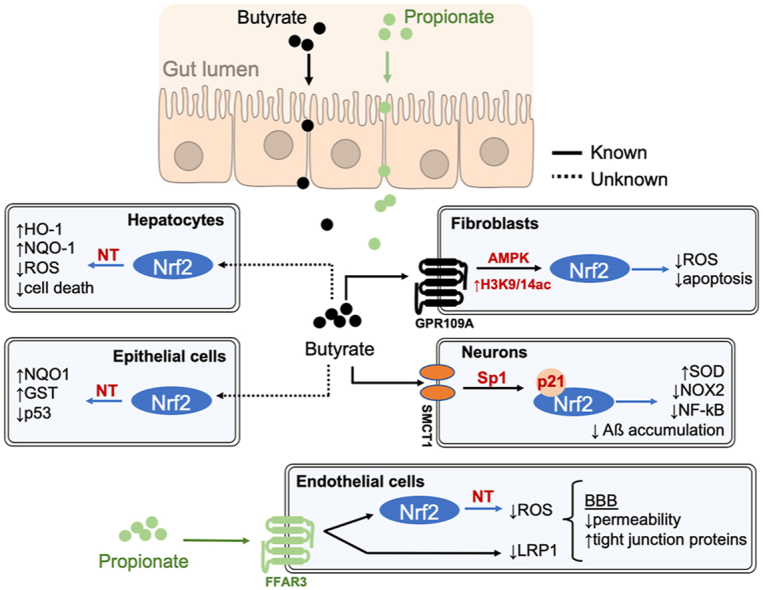
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), produced by colonic bacteria and obtained from the diet, have been linked to beneficial effects on human health associated with their metabolic and signaling properties. Their physiological functions are related to their aliphatic tail length and dependent on the activation of specific membrane receptors. In this review, we focus on the mechanisms underlying SCFAs mediated protection against oxidative and mitochondrial stress and their role in regulating metabolic pathways in specific tissues. We critically evaluate the evidence for their cytoprotective roles in suppressing inflammation and carcinogenesis and the consequences of aging. The ability of these natural compounds to induce signaling pathways, involving nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), contributes to the maintenance of redox homeostasis under physiological conditions. SCFAs may thus serve as nutritional and therapeutic agents in healthy aging and in vascular and other diseases such as diabetes, neuropathologies and cancer.
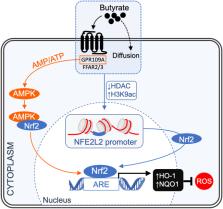
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
SCFAs are a link between the microbiota, redox signaling and host metabolism.
-
•
SCFAs modulate Nrf2 redox signaling through specific free fatty acid receptors.
-
•
Butyrate induces epigenetic regulation and/or Nrf2 nuclear translocation.
-
•
Butyrate and propionate protect the blood-brain barrier by facilitating docosahexaenoic acid transport.
-
•
Regulation of redox homeostasis by SCFAs supports their potential as therapeutic nutrients in health and disease.
Related collections
Most cited references145
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found