- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Quantum Confined High-Entropy Lanthanide Oxysulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals

Read this article at
Abstract
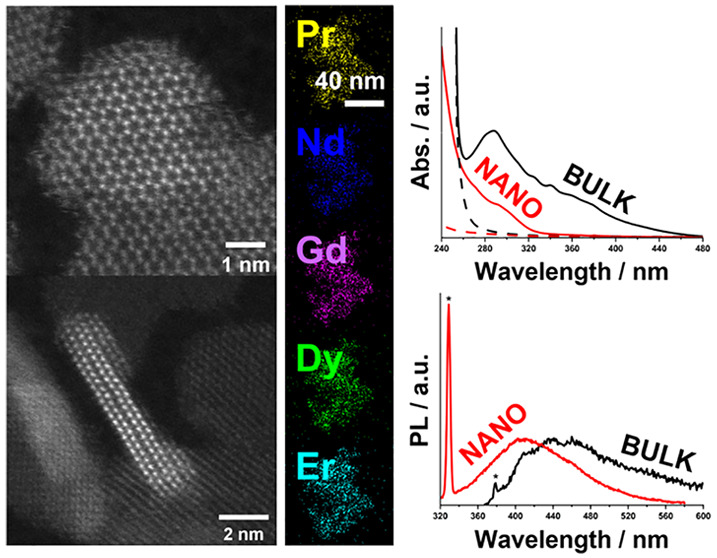
We have synthesized the first reported example of quantum confined high-entropy (HE) nanoparticles, using the lanthanide oxysulfide, Ln 2SO 2, system as the host phase for an equimolar mixture of Pr, Nd, Gd, Dy, and Er. A uniform HE phase was achieved via the simultaneous thermolysis of a mixture of lanthanide dithiocarbamate precursors in solution. This was confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction and high-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy, with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopic mapping confirming the uniform distribution of the lanthanides throughout the particles. The nanoparticle dispersion displayed a significant blue shift in the absorption and photoluminescence spectra relative to our previously reported bulk sample with the same composition, with an absorption edge at 330 nm and a λ max at 410 nm compared to the absorption edge at 500 nm and a λ max at 450 nm in the bulk, which is indicative of quantum confinement. We support this postulate with experimental and theoretical analysis of the bandgap energy as a function of strain and surface effects (ligand binding) as well as calculation of the exciton Bohr radiii of the end member compounds.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found