- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fulminant demyelinating encephalomyelitis : Insights from antibody studies and neuropathology
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives:
Antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) are detectable in inflammatory demyelinating CNS diseases, and MOG antibody–associated diseases seem to have a better prognosis despite occasionally severe presentations.
Methods:
We report the case of a 71-year-old patient with acute visual and gait disturbance that dramatically worsened to bilateral amaurosis, tetraplegia, and respiratory insufficiency within a few days.
Results:
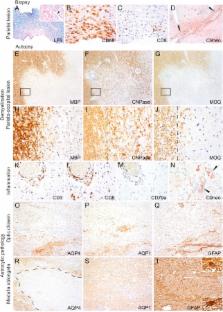
MRI showed multiple progressive cerebral and spinal lesions with diffusion restriction (including both optic nerves) and marginal contrast enhancement. Routine blood and CSF measures including oligoclonal bands were normal. At disease onset, MOG immunoglobulin G was detected (serum titer 1:1,280, corresponding CSF titer was 1:20) and remained positive in patient serum. Aquaporin-4 antibodies were absent at disease onset but seroconverted to positive at week 9. In addition, CSF glial fibrillary acid protein and myelin basic protein levels were very high at onset but decreased during disease course. After 4 months, the patient died despite immunomodulatory treatment. Postmortem neuropathologic examination revealed an acute multiple sclerosis (MS) defined by multiple demyelinating lesions with a pronounced destructive component and loss of astrocytes. Lesion pattern of optic chiasm met MS pattern II characterized by antibody and complement-mediated demyelination.
Conclusion:
The case with the clinical presentation of an acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis with predominant optic and spinal involvement, absent oligoclonal bands, a histopathology of acute MS pattern II and development of aquaporin-4 antibodies extends the spectrum of MOG antibody–associated encephalomyelitis. Although, MOG antibodies are suspected to indicate a favorable prognosis, fulminant disease courses are possible and warrant an aggressive immunotherapy.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Overlapping demyelinating syndromes and anti–N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MOG cell-based assay detects non-MS patients with inflammatory neurologic disease
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies in adults with a neuromyelitis optica phenotype.
Author and article information
Contributors
-
PLOS ONE, academic editor, 2012-Current Medicinal Chemistry, editorial board, 2006-2012 Autoimmune Diseases, 2012-2013
-
The University Hospital and Medical University of Innsbruck (Austria, Markus Reindl) receive payments for antibody assays (NMDAR, AQP4 and other autoantibodies) and for AQP4 antibody validation experiments organized by Euroimmun.
-
(1) This study was supported by a research grant from the Austrian Federal Ministery of Science and Economy (grant BIG WIG MS).
-
(1) Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science & Technology (MEXT) in Japan, Japanese Government Scholarship Program, 4 years (2010 - 2014)
-
(1) Grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI 15K19472) (2) Research support from CAPES/Brasil (88881.068012/2014)
-
Serves on scientific advisory boards for Bayer Schering Pharma, Biogen Idec, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Novartis Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Nihon Pharmaceutical, Merck Serono, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Medimmune and Medical Review.
-
has received funding for travel and speaker honoraria from Bayer Schering Pharma, Biogen Idec, Eisai Inc., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Novartis Pharma, Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Asahi Kasei Medical Co., Daiichi Sankyo, and Nihon Pharmaceutical.
-
Serve as an editorial board member of Clinical and Experimental Neuroimmunology (2009-present) and a advisory board member of Sri Lanka journal of Neurology.
-
has received research support from Bayer Schering Pharma, Biogen Idec Japan, Asahi Kasei Medical, The Chemo-Sero-Therapeutic Research Institute, Teva Pharmaceutical, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Teijin Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical,Ono Pharmaceutical, Nihon Pharmaceutical, and Genzyme Japan.
-
funded as the investigator (2010?present) by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology of Japan and as the secondary investigator by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Labor of Japan (2010?present).
-
I have received speaker and travel honoraria for several scientific meetings from Biogen Idec, Novartis and Teva.
-
I am member of the Editorial Board of several Journals in the fields of Neurology and Neuroscience.
-
Austrian Science Fund, Projects P19854, P 24245;principal investigator; 2007-2012 European Union FP7 Project Neuroprmise Pl 018637 2007-2011; Subproject; E-Rare Project EDEN; 2011-2014; subproject This funding is not directly related to the respective article
Journal
Affiliations
Author notes
Funding information and disclosures are provided at the end of the article. Go to Neurology.org/nn for full disclosure forms. The Article Processing Charge was paid by authors.
Article
Publisher ID: NEURIMMINFL2015007252This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives License 4.0 (CC BY-NC-ND), which permits downloading and sharing the work provided it is properly cited. The work cannot be changed in any way or used commercially.