- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Serotonin Transporter and Plasma Membrane Monoamine Transporter Are Necessary for the Antidepressant-Like Effects of Ketamine in Mice
Read this article at
Abstract
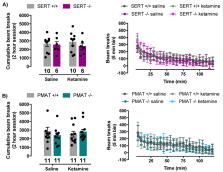
Major depressive disorder is typically treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), however, SSRIs take approximately six weeks to produce therapeutic effects, if any. Not surprisingly, there has been great interest in findings that low doses of ketamine, a non-competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, produce rapid and long-lasting antidepressant effects. Preclinical studies show that the antidepressant-like effects of ketamine are dependent upon availability of serotonin, and that ketamine increases extracellular serotonin, yet the mechanism by which this occurs is unknown. Here we examined the role of the high-affinity, low-capacity serotonin transporter (SERT), and the plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT), a low-affinity, high-capacity transporter for serotonin, as mechanisms contributing to ketamine’s ability to increase extracellular serotonin and produce antidepressant-like effects. Using high-speed chronoamperometry to measure real-time clearance of serotonin from CA3 region of hippocampus in vivo, we found ketamine robustly inhibited serotonin clearance in wild-type mice, an effect that was lost in mice constitutively lacking SERT or PMAT. As expected, in wild-type mice, ketamine produced antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test. Mapping onto our neurochemical findings, the antidepressant-like effects of ketamine were lost in mice lacking SERT or PMAT. Future research is needed to understand how constitutive loss of either SERT or PMAT, and compensation that occurs in other systems, is sufficient to void ketamine of its ability to inhibit serotonin clearance and produce antidepressant-like effects. Taken together with existing literature, a critical role for serotonin, and its inhibition of uptake via SERT and PMAT, cannot be ruled out as important contributing factors to ketamine’s antidepressant mechanism of action. Combined with what is already known about ketamine’s action at NMDA receptors, these studies help lead the way to the development of drugs that lack ketamine’s abuse potential but have superior efficacy in treating depression.
Related collections
Most cited references81
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
NMDA Receptor Blockade at Rest Triggers Rapid Behavioural Antidepressant Responses
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found