- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Electrophysiological response to omitted stimulus in sentence processing
Read this article at
Abstract
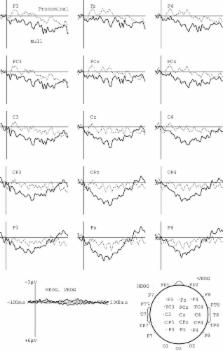
The current study provides evidence that the absence of a syntactically expected item leads to a sustained cognitive processing demand. Event-related potentials were measured at the omission of a syntactically expected object argument in a speech sequence. English monolingual adults listened to paired sentences. The first sentence in the pair established a context. The second sentence provided a response to the first sentence that was either grammatically correct by containing an overt object argument in the form of a pronoun, or was syntactically unacceptable by omitting the expected object pronoun. Event-related potentials measured at the omission of the object argument showed a prolonged positivity for 100–600 ms with a broad scalp distribution, and for 600–1000 ms with a focus in the anterior region. This observed omitted stimulus potential may contain characteristics of the P300 component, associated with the detection of the deviation of an expected stimulus, and the classical P600 related to syntactic reanalysis. Further, the late anterior P600 may indicate an increased memory demand in sentence comprehension. Thus, this linguistic omitted stimulus potential is a cognitive indicator of language processing that can be used to investigate the organization of linguistic knowledge.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Temporal structure of syntactic parsing: early and late event-related brain potential effects.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found