- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long non-coding RNAs: Biogenesis, functions, and clinical significance in gastric cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most prevalent malignant tumor types and the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Its morbidity and mortality are very high due to a lack of understanding about its pathogenesis and the slow development of novel therapeutic strategies. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs with a length of more than 200 nt. They play crucial roles in a wide spectrum of physiological and pathological processes by regulating the expression of genes involved in proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, cell cycle, invasion, metastasis, DNA damage, and carcinogenesis. The aberrant expression of lncRNAs has been found in various cancer types. A growing amount of evidence demonstrates that lncRNAs are involved in many aspects of GC pathogenesis, including its occurrence, metastasis, and recurrence, indicating their potential role as novel biomarkers in the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic targets of GC. This review systematically summarizes the biogenesis, biological properties, and functions of lncRNAs and highlights their critical role and clinical significance in GC. This information may contribute to the development of better diagnostics and treatments for GC.
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
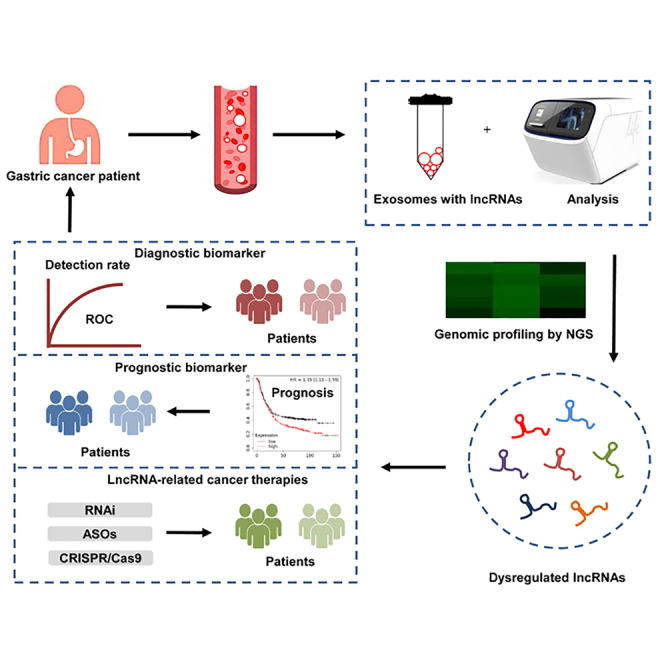
In this article, Liu et al. summarize the biological features, biogenesis, and functions of lncRNAs and focus on their mechanisms in gastric cancer (GC) progression and their potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for GC.
Related collections
Most cited references195
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found