- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Feasibility of using the Vero SBRT system for intracranial SRS
Read this article at
Abstract
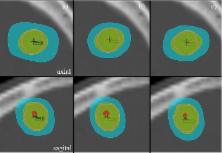
The Vero SBRT system was benchmarked in a planning study against the Novalis SRS system for quality of delivered dose distributions to intracranial lesions and assessing the Vero system's capacity for SRS. A total of 27 patients with one brain lesion treated on the Novalis system, with 3 mm leaf width MLC and C‐arm gantry, were replanned for Vero, with a 5 mm leaf width MLC mounted on an O‐ring gantry allowing rotations around both the horizontal and vertical axis. The Novalis dynamic conformal arc (DCA) planning included vertex arcs, using 90° couch rotation. These vertex arcs cannot be reproduced with Vero due to the mechanical limitations of the O‐ring gantry. Alternative class solutions were investigated for the Vero. Additionally, to distinguish between the effect of MLC leaf width and different beam arrangements on dose distributions, the Vero class solutions were also applied for Novalis. In addition, the added value of noncoplanar IMRT was investigated in this study. Quality of the achieved dose distributions was expressed in the conformity index (CI) and gradient index (GI), and compared using a paired Student's t‐test with statistical significance for p‐values . For lesions larger than 5 cm 3, no statistical significant difference in conformity was observed between Vero and Novalis, but for smaller lesions, the dose distributions showed a significantly better conformity for the Novalis mainly due to the smaller MLC leaf width. Using IMRT on Vero reduces this conformity difference to nonsignificant levels. The cutoff for achieving a GI around 3, characterizing a sharp dose falloff outside the target volume was 4 cm 3 for Novalis and 7 cm 3 for Vero using DCA technique. Using noncoplanar IMRT, this threshold was reduced to 3 cm 3 for the Vero system. The smaller MLC and the presence of the vertex fields allow the Novalis system to better conform the dose around the lesion and to obtain steeper dose falloff outside the lesion. Comparable dosimetric characteristics can be achieved with Vero for lesions larger than 3 cm 3 and using IMRT.
PACS number: 87.55.D
Related collections
Most cited references17
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Innovations in image-guided radiotherapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found