- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sertoli cell-conditioned medium can improve blood-testis-barrier function and spermatogenesis in azoospermia mice induced by scrotal hyperthermia: An experimental study
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
An increase in the temperature of the testis is associated with damage to the epithelium of seminiferous tubules and disruption of sperm production.
Objective
The current study aimed to investigate the effect of the Sertoli cell-conditioned medium (SCCM) on the blood-testis-barrier associated genes and spermatogenesis process following scrotal hyperthermia.
Materials and Methods
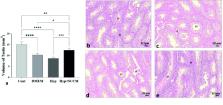
In this experimental study, 40 adult NMRI mice (8 wk, 25–30 gr) were allocated into 4 groups: I) control, II) DMEM (10 μl Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium), III) scrotal hyperthermia, and IV) scrotal hyperthermia+SCCM (10 μl SCCM). Hyperthermia was induced by placing the mice scrotum in water at 43 C for 20 min every other day for 10 days. Mice were treated every other day for 5 wk. Then the animals were euthanized, and the tails of epididymis were removed to analyze sperm parameters, testis were taken for stereological assessment, reactive oxygen spices and glutathione levels, and the expression of Ocln, Gja1, Cdh2, and Itgb1.
Results
The results of sperm analysis indicated that SCCM-treated mice significantly increased sperm count and motility and reduced DNA fragmentation. In addition, histological and molecular findings showed that the volume of testicular tissue, the number of germ cells, the glutathione level, and the expression of Ocln, Gja1, Cdh2, and Itgb1 genes were significantly increased in the SCCM-treated mice.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Precocious puberty
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Review of Intraperitoneal Injection of Sodium Pentobarbital as a Method of Euthanasia in Laboratory Rodents
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found