- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Positive Surgical Margins in the 10 Most Common Solid Cancers
Read this article at
Abstract
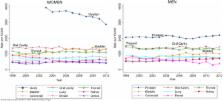
A positive surgical margin (PSM) following cancer resection oftentimes necessitates adjuvant treatments and carries significant financial and prognostic implications. We sought to compare PSM rates for the ten most common solid cancers in the United States, and to assess trends over time. Over 10 million patients were identified in the National Cancer Data Base from 1998–2012, and 6.5 million had surgical margin data. PSM rates were compared between two time periods, 1998–2002 and 2008–2012. PSM was positively correlated with tumor category and grade. Ovarian and prostate cancers had the highest PSM prevalence in women and men, respectively. The highest PSM rates for cancers affecting both genders were seen for oral cavity tumors. PSM rates for breast cancer and lung and bronchus cancer in both men and women declined over the study period. PSM increases were seen for bladder, colon and rectum, and kidney and renal pelvis cancers. This large-scale analysis appraises the magnitude of PSM in the United States in order to focus future efforts on improving oncologic surgical care with the goal of optimizing value and improving patient outcomes.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Carcinoma of the corpus uteri. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the Results of Treatment in Gynecological Cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found