- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Predicting dyslipidemia incidence: unleashing machine learning algorithms on Lifestyle Promotion Project data
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Dyslipidemia, characterized by variations in plasma lipid profiles, poses a global health threat linked to millions of deaths annually.
Objectives
This study focuses on predicting dyslipidemia incidence using machine learning methods, addressing the crucial need for early identification and intervention.
Methods
The dataset, derived from the Lifestyle Promotion Project (LPP) in East Azerbaijan Province, Iran, undergoes a comprehensive preprocessing, merging, and null handling process. Target selection involves five distinct dyslipidemia-related variables. Normalization techniques and three feature selection algorithms are applied to enhance predictive modeling.
Result
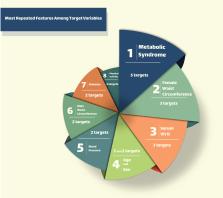
The study results underscore the potential of different machine learning algorithms, specifically multi-layer perceptron neural network (MLP), in reaching higher performance metrics such as accuracy, F1 score, sensitivity and specificity, among other machine learning methods. Among other algorithms, Random Forest also showed remarkable accuracies and outperformed K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) in metrics like precision, recall, and F1 score. The study’s emphasis on feature selection detected meaningful patterns among five target variables related to dyslipidemia, indicating fundamental shared unities among dyslipidemia-related factors. Features such as waist circumference, serum vitamin D, blood pressure, sex, age, diabetes, and physical activity related to dyslipidemia.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Overview of artificial intelligence in medicine
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found