- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
GRP78 in lung cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
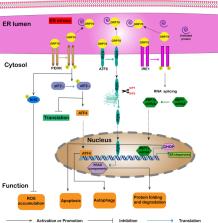
Glucose-regulating protein 78 (GRP78) is a molecular chaperone in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that promotes folding and assembly of proteins, controls the quality of proteins, and regulates ER stress signaling through Ca 2+ binding to the ER. In tumors, GRP78 is often upregulated, acting as a central stress sensor that senses and adapts to changes in the tumor microenvironment, mediating ER stress of cancer cells under various stimulations of the microenvironment to trigger the folding protein response. Increasing evidence has shown that GRP78 is closely associated with the progression and poor prognosis of lung cancer, and plays an important role in the treatment of lung cancer. Herein, we reviewed for the first time the functions and mechanisms of GRP78 in the pathological processes of lung cancer, including tumorigenesis, apoptosis, autophagy, progression, and drug resistance, giving a comprehensive understanding of the function of GRP78 in lung cancer. In addition, we also discussed the potential role of GRP78 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for lung cancer, which is conducive to improving the assessment of lung cancer and the development of new therapeutic interventions.
Related collections
Most cited references132
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found