- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Health Impacts of the Built Environment: Within-Urban Variability in Physical Inactivity, Air Pollution, and Ischemic Heart Disease Mortality
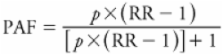
Read this article at
Abstract
Background: Physical inactivity and exposure to air pollution are important risk factors for death and disease globally. The built environment may influence exposures to these risk factors in different ways and thus differentially affect the health of urban populations.
Objective: We investigated the built environment’s association with air pollution and physical inactivity, and estimated attributable health risks.
Methods: We used a regional travel survey to estimate within-urban variability in physical inactivity and home-based air pollution exposure [particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter ≤ 2.5 μm (PM 2.5), nitrogen oxides (NO x), and ozone (O 3)] for 30,007 individuals in southern California. We then estimated the resulting risk for ischemic heart disease (IHD) using literature-derived dose–response values. Using a cross-sectional approach, we compared estimated IHD mortality risks among neighborhoods based on “walkability” scores.
Results: The proportion of physically active individuals was higher in high- versus low-walkability neighborhoods (24.9% vs. 12.5%); however, only a small proportion of the population was physically active, and between-neighborhood variability in estimated IHD mortality attributable to physical inactivity was modest (7 fewer IHD deaths/100,000/year in high- vs. low-walkability neighborhoods). Between-neighborhood differences in estimated IHD mortality from air pollution were comparable in magnitude (9 more IHD deaths/100,000/year for PM 2.5 and 3 fewer IHD deaths for O 3 in high- vs. low-walkability neighborhoods), suggesting that population health benefits from increased physical activity in high-walkability neighborhoods may be offset by adverse effects of air pollution exposure.
Policy implications: Currently, planning efforts mainly focus on increasing physical activity through neighborhood design. Our results suggest that differences in population health impacts among neighborhoods are similar in magnitude for air pollution and physical activity. Thus, physical activity and exposure to air pollution are critical aspects of planning for cleaner, health-promoting cities.
Related collections
Most cited references52
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution: epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long-term ozone exposure and mortality.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found