- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cooperative Regulation of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma by Nicotinic and Beta-Adrenergic Receptors: A Novel Target for Intervention
Read this article at
Abstract
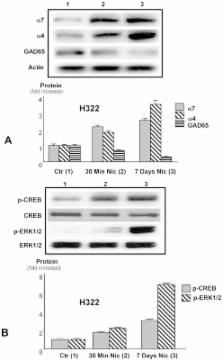
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death; 80–85% of lung cancer cases are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Smoking is a documented risk factor for the development of this cancer. Although nicotine does not have the ability to initiate carcinogenic events, recent studies have implicated nicotine in growth stimulation of NSCLC. Using three NSCLC cell lines (NCI-H322, NCI-H441 and NCI-H1299), we identified the cooperation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) and β-adrenergic receptors (β-ARs) as principal regulators of these effects. Proliferation was measured by thymidine incorporation and MTT assays, and Western blots were used to monitor the upregulation of the nAChRs and activation of signaling molecules. Noradrenaline and GABA were measured by immunoassays. Nicotine-treated NSCLC cells showed significant induction of the α7nAChR and α4nAChR, along with significant inductions of p-CREB and p-ERK1/2 accompanied by increases in the stress neurotransmitter noradrenaline, which in turn led to the observed increase in DNA synthesis and cell proliferation. Effects on cell proliferation and signaling proteins were reversed by the α7nAChR antagonist α-BTX or the β-blocker propranolol. Nicotine treatment also down-regulated expression of the GABA synthesizing enzyme GAD 65 and the level of endogenous GABA, while treatment of NSCLC cells with GABA inhibited cell proliferation. Interestingly, GABA acts by reducing β-adrenergic activated cAMP signaling. Our findings suggest that nicotine-induced activation of this autocrine noradrenaline-initiated signaling cascade and concomitant deficiency in inhibitory GABA, similar to modulation of these neurotransmitters in the nicotine-addicted brain, may contribute to the development of NSCLC in smokers. Our data suggest that exposure to nicotine either by tobacco smoke or nicotine supplements facilitates growth and progression of NSCLC and that pharmacological intervention by β blocker may lower the risk for NSCLC development among smokers and could be used to enhance the clinical outcome of standard cancer therapy.
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cancer statistics, 2007.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Acetylcholine beyond neurons: the non-neuronal cholinergic system in humans.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found