- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Rubus fairholmianus Root Extract and Their Activity against Pathogenic Bacteria
Read this article at
Abstract
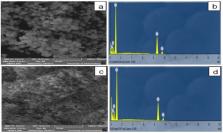
Recently, the biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) from crude extracts and phytochemicals has attracted much attention. Green synthesis of NPs is cost-effective, eco-friendly, and is a promising alternative for chemical synthesis. This study involves ZnO NPs synthesis using Rubus fairholmianus root extract (RE) as an efficient reducing agent. The UV spectrum of RE-ZnO NPs exhibited a peak at 357 nm due to intrinsic bandgap absorption and an XRD pattern that matches the ZnO crystal structure (JCPDS card no: 36-1451). The average particle size calculated from the Debye–Scherrer equation is 11.34 nm. SEM analysis showed that the RE-ZnO NPs spherical in shape with clusters (1–100 nm). The antibacterial activity of the NPs was tested against Staphylococcus aureus using agar well diffusion, minimum inhibitory concentration, and bacterial growth assay. The R. fairholmianus phytochemicals facilitate the synthesis of stable ZnO NPs and showed antibacterial activity.
Related collections
Most cited references45

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metal-Based Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: An Overview
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found