- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Preparation, characterization, and in vivo pharmacokinetics of nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin
Abstract
Background
The purpose of this work was to develop nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) loaded simultaneously with oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin.
Methods
An aqueous dispersion of NLCs was prepared successfully using a film-ultrasonic method, with glycerin monostearate as the solid lipid and oleic acid as the liquid lipid. Poloxamer 188 was used as the surfactant. A central composite design was used to optimize the technologic parameters. The characteristics of the NLCs were then investigated.
Results
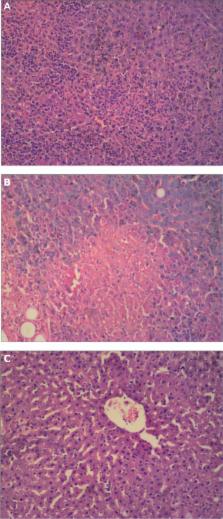
The encapsulation efficiency was 48.34% ± 2.76%, drug loading was 8.06% ± 0.42%, particle size was 111.0 ± 1.56 nm, polydispersity index was 0.287 ± 0.01, and zeta potential was −23.8 ± 0.36 mV for the optimized NLCs. The other physicochemical properties were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Drug release followed first-order kinetics and release studies confirmed that oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin fitted a sustained-release model. Compared with NLCs loaded with oleanolic acid or gentiopicrin alone, NLCs loaded with both oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin produced drug concentrations which persisted for a significantly longer time in plasma, with a linear decrement following second-order kinetics. Aspartate and alanine aminotransferase levels were significantly lower on exposure to NLCs loaded with both oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin than in negative controls.
Conclusion
The results of this study confirm that oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin can be loaded simultaneously into NLCs. Compared with oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin loaded alone, sustained release and protective effects against hepatic injury were observed using NLCs loaded with both oleanolic acid and gentiopicrin.
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) coated with Chitosan Oligosaccharides and its potential use in ocular drug delivery system.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found