- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Accelerating COVID-19 Research Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation

Abstract
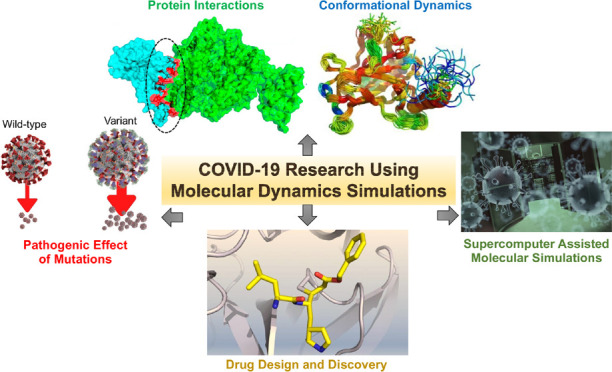
The COVID-19 pandemic has emerged as a global medico-socio-economic disaster. Given the lack of effective therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2, scientists are racing to disseminate suggestions for rapidly deployable therapeutic options, including drug repurposing and repositioning strategies. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations have provided the opportunity to make rational scientific breakthroughs in a time of crisis. Advancements in these technologies in recent years have become an indispensable tool for scientists studying protein structure, function, dynamics, interactions, and drug discovery. Integrating the structural data obtained from high-resolution methods with MD simulations has helped in comprehending the process of infection and pathogenesis, as well as the SARS-CoV-2 maturation in host cells, in a short duration of time. It has also guided us to identify and prioritize drug targets and new chemical entities, and to repurpose drugs. Here, we discuss how MD simulation has been explored by the scientific community to accelerate and guide translational research on SARS-CoV-2 in the past year. We have also considered future research directions for researchers, where MD simulations can help fill the existing gaps in COVID-19 research.
Related collections
Most cited references83
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular Dynamics Simulation for All
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found