- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ubiquitin-specific protease 3 attenuates interleukin-1β-mediated chondrocyte senescence by deacetylating forkhead box O-3 via sirtuin-3
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
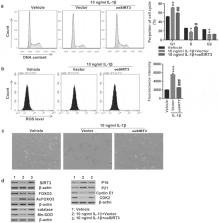
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects approximately 12% of the aging Western population. The sirtuin/forkhead box O (SIRT/FOXO) signaling pathway plays essential roles in various biological processes. Despite it has been demonstrated that ubiquitin-specific protease 3 (USP3) inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis induced by interleukin (IL)-1β, the role of USP3/SIRT3/FOXO3 in the senescence of chondrocytes in OA is unclear. This study initially isolated articular chondrocytes and investigated the role of USP3 in IL-1β-induced senescence of chondrocytes. After USP3 was overexpressed or silenced by lentivirus, expressions of genes and proteins were detected using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunoblotting, respectively. Cell cycle analysis was performed using flow cytometry. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and senescence were analyzed. Then, SIRT3 was inhibited or overexpressed to explore the underlying mechanism. We found that overexpression of USP3 hindered IL-1β-mediated cell cycle arrest, ROS generation, and chondrocyte senescence. The inhibition of SIRT3 blocked the protective effect of USP3 on cell senescence, whereas the overexpression of SIRT3 abolished USP3-silencing-induced cell senescence. Furthermore, SIRT3 attenuated cell senescence, probably by deacetylating FOXO3. USP3 upregulated SIRT3 to deacetylate FOXO3 and attenuated IL-1β-induced chondrocyte senescence. This study demonstrated that USP3 probably attenuated IL-1β-mediated chondrocyte senescence by deacetylating FOXO3 via SIRT3.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Role of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis
