- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Intermediate C9orf72 alleles in neurological disorders: does size really matter?
Read this article at
Abstract
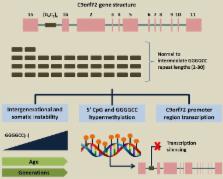
C9orf72 repeat expansions is a major cause of familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) worldwide. Sizes of <20 hexanucleotide repeats are observed in controls, while up to thousands associate with disease. Intermediate C9orf72 repeat lengths, however, remain uncertain. We systematically reviewed the role of intermediate C9orf72 alleles in C9orf72-related neurological disorders. We identified 49 studies with adequate available data on normal or intermediate C9orf72 repeat length, involving subjects with FTD, ALS, Parkinson’s disease (PD), atypical parkinsonism, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other aetiologies. We found that, overall, normal or intermediate C9orf72 repeat lengths are not associated with higher disease risk across these disorders, but intermediate allele sizes appear to associate more frequently with neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Intermediate sizes were detected in subjects with personal or family history of FTD and/or psychiatric illness, parkinsonism complicated by psychosis and rarely in psychiatric cohorts. Length of the hexanucleotide repeat may be influenced by ethnicity (with Asian controls displaying shorter normal repeat lengths compared with Caucasians) and underlying haplotype, with more patients and controls carrying the ‘risk’ haplotype rs3849942 displaying intermediate alleles. There is some evidence that intermediate alleles display increased methylation levels and affect normal transcriptional activity of the C9orf72 promoter, but the ‘critical’ repeat size required for initiation of neurodegeneration remains unknown and requires further study. In common neurological diseases, intermediate C9orf72 repeats do not influence disease risk but may associate with higher frequency of neuropsychiatric symptoms. This has important clinical relevance as intermediate carriers pose a challenge for genetic counselling.
Related collections
Most cited references49

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Pan-European Study of the C9orf72 Repeat Associated with FTLD: Geographic Prevalence, Genomic Instability, and Intermediate Repeats
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hypermethylation of the CpG island near the G4C2 repeat in ALS with a C9orf72 expansion.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found