- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
pH-Responsive Pluronic F127–Lenvatinib-Encapsulated Halogenated Boron-Dipyrromethene Nanoparticles for Combined Photodynamic Therapy and Chemotherapy of Liver Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract

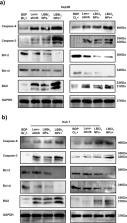
Combination therapy such as photodynamic therapy (PDT)-enhanced chemotherapy is regarded as a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Boron-dipyrromethene (BODIPY), as close relatives of porphyrins, was widely used in PDT. However, poor water solubility, rapid metabolism by the body and lack of targeting limits its clinical application. Lenvatinib, as the first-line drug for molecular-targeted therapy of liver cancer, restricted its clinical application for its side effects. Herein, to achieve the synergy between PDT and chemotherapy, we synthesized two halogenated BODIPY, BDPBr 2 and BDPCl 2, which were prepared into self-assembly nanoparticles with lenvatinib, and were encapsulated with Pluronic F127 through the nanoprecipitation method, namely, LBPNPs (LBBr 2 NPs and LBCl 2 NPs). The fluorescence quantum yields of LBPNPs were 0.73 and 0.71, respectively. The calculated loading rates of lenvatinib for LBBr 2 NPs and LBCl 2 NPs were 11.8 and 10.2%, respectively. LBPNPs can be hydrolyzed under weakly acidic conditions (pH 5.0) to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and the release rate of lenvatinib reached 88.5 and 82.4%. Additionally, LBPNPs can be effectively taken up by Hep3B and Huh7 liver cancer cells, releasing halogenated BODIPY and lenvatinib in the acidic environment of tumor cells to enhance the targeting performance of chemotherapeutics. Compared with free lenvatinib and separate halogenated BODIPY, LBPNPs can inhibit tumor growth more effectively through pH-responsive chemo/photodynamic synergistic therapy and significantly promote the cascade of caspase apoptotic protease. This study shows that LBPNPs can be a promising nanotheranostic agent for synergetic chemo/photodynamic liver cancer therapy.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found