- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ultrafast spontaneous emission source using plasmonic nanoantennas

Read this article at
Abstract
Typical emitters such as molecules, quantum dots and semiconductor quantum wells have slow spontaneous emission with lifetimes of 1–10 ns, creating a mismatch with high-speed nanoscale optoelectronic devices such as light-emitting diodes, single-photon sources and lasers. Here we experimentally demonstrate an ultrafast (<11 ps) yet efficient source of spontaneous emission, corresponding to an emission rate exceeding 90 GHz, using a hybrid structure of single plasmonic nanopatch antennas coupled to colloidal quantum dots. The antennas consist of silver nanocubes coupled to a gold film separated by a thin polymer spacer layer and colloidal core–shell quantum dots, a stable and technologically relevant emitter. We show an increase in the spontaneous emission rate of a factor of 880 and simultaneously a 2,300-fold enhancement in the total fluorescence intensity, which indicates a high radiative quantum efficiency of ∼50%. The nanopatch antenna geometry can be tuned from the visible to the near infrared, providing a promising approach for nanophotonics based on ultrafast spontaneous emission.
Abstract
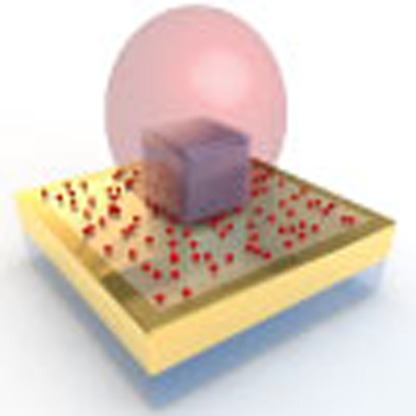 Typical emitters such as molecules and quantum dots have slow spontaneous emission
with lifetimes of 1–10 ns. Here, Hoang
et al. have fabricated a hybrid structure of plasmonic nanopatch antennas coupled to quantum
dots, achieving ultrafast spontaneous emission with a lifetime of 11 ps.
Typical emitters such as molecules and quantum dots have slow spontaneous emission
with lifetimes of 1–10 ns. Here, Hoang
et al. have fabricated a hybrid structure of plasmonic nanopatch antennas coupled to quantum
dots, achieving ultrafast spontaneous emission with a lifetime of 11 ps.
Related collections
Most cited references27
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Quantum nature of a strongly-coupled single quantum dot-cavity system
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lasing action in strongly coupled plasmonic nanocavity arrays.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found