- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Codesigning a Measure of Person-Centred Coordinated Care to Capture the Experience of the Patient : The Development of the P3CEQ
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
Person-centred coordinated care (P3C) is a priority for stakeholders (ie, patients, carers, professionals, policy makers). As a part of the development of an evaluation framework for P3C, we set out to identify patient-reported experience measures (PREMs) suitable for routine measurement and feedback during the development of services.
Methods:
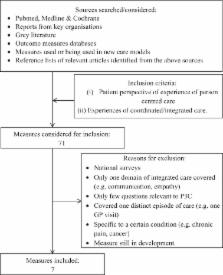
A rapid review of the literature was undertaken to identity existing PREMs suitable for the probing person-centred and/or coordinated care. Of 74 measures identified, 7 met our inclusion criteria. We critically examined these against core domains and subdomains of P3C. Measures were then presented to stakeholders in codesign workshops to explore acceptability, utility, and their strengths/weaknesses.
Results:
The Long-Term Condition 6 questionnaire was preferred for its short length, utility, and tone. However, it lacked key questions in each core domain, and in response to requests from our codesign group, new questions were added to cover consideration as a whole person, coordination, care plans, carer involvement, and a single coordinator. Cognitive interviews, on-going codesign, and mapping to core P3C domains resulted in the refinement of the questionnaire to 11 items with 1 trigger question. The 11-item modified version was renamed the P3C Experiences Questionnaire.
Conclusions:
Due to a dearth of brief measures available to capture people’s experience of P3C for routine practice, an existing measure was modified using an iterative process of adaption and validation through codesign workshops. Next steps include psychometric validation and modification for people with dementia and learning difficulties.
Related collections
Most cited references23
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Development and validation of the Patient Assessment of Chronic Illness Care (PACIC).
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found