- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant

Read this article at
Abstract
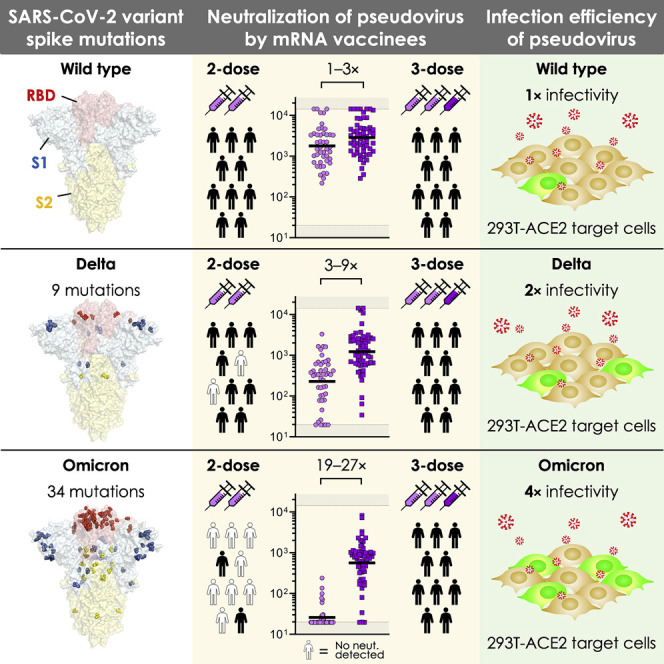
Recent surveillance has revealed the emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (BA.1/B.1.1.529) harboring up to 36 mutations in spike protein, the target of neutralizing antibodies. Given its potential to escape vaccine-induced humoral immunity, we measured the neutralization potency of sera from 88 mRNA-1273, 111 BNT162b, and 40 Ad26.COV2.S vaccine recipients against wild-type, Delta, and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses. We included individuals that received their primary series recently (<3 months), distantly (6–12 months), or an additional “booster” dose, while accounting for prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. Remarkably, neutralization of Omicron was undetectable in most vaccinees. However, individuals boosted with mRNA vaccines exhibited potent neutralization of Omicron, only 4–6-fold lower than wild type, suggesting enhanced cross-reactivity of neutralizing antibody responses. In addition, we find that Omicron pseudovirus infects more efficiently than other variants tested. Overall, this study highlights the importance of additional mRNA doses to broaden neutralizing antibody responses against highly divergent SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Graphical abstract
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant pseudovirus exhibits escape from vaccine-induced humoral immunity. However, a third dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine elicited humoral immunity capable of cross-neutralizing this strain. In addition, pseudovirus produced with the Omicron spike exhibited more efficient transduction of ACE2-expressing target cells than other variants.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found