- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The prevalence and severity of 25-(OH)-vitamin D insufficiency in HCV infected and in HBV infected patients: a prospective study
Read this article at
Abstract
Aim of the study
To assess the prevalence and severity of vitamin D insufficiency in patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
Material and methods
This prospective study included 90 patients with chronic hepatitis C and 35 patients with chronic hepatitis B admitted to the Infectious Diseases Department between March 2013 and May 2014. Patients with chronic liver disease other than viral hepatitis, HIV co-infection, advanced liver disease and a history of diseases influencing vitamin D status were excluded. Serum vitamin D measurement as well as liver function, viral load, HCV genotype, interleukin 28 and liver fibrosis assessments were performed.
Results
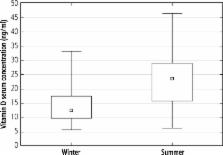
In all patients, the mean vitamin D serum concentration was 18.8 (± 8.9) ng/ml. The mean vitamin D level in HBV infected patients was lower than in HCV infected patients (17.6 ng/ml vs. 19.3 ng/ml; p = 0.43). Vitamin D status was assessed in relation to viral load, HCV genotype, interleukin 28 and sex, but the differences were not significant. In both groups, serum vitamin D levels were significantly lower in winter compared to summer (14.2 ng/ml vs. 23.9 ng/ml in patients infected with HCV [ p < 0.000001] and 14.7 ng/ml vs. 23.8 ng/ml in patients infected with HBV [ p < 0.001]).
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Low vitamin D serum concentration is associated with high levels of hepatitis B virus replication in chronically infected patients.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found