- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Delayed Presentation of Berardinelli-Siep Lipodystrophy in an Adolescent Female

Read this article at
Abstract
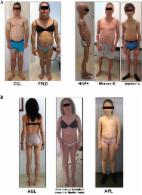
Berardinelli-Siep syndrome (BSS) is a form of congenital generalized lipodystrophy that disrupts the pathways of lipid metabolism. It presents with physical exam findings, including muscular hypertrophy and lipoatrophy as well as serious metabolic consequences such as diabetes mellitus, hypertriglyceridemia, acute pancreatitis, hepatomegaly, and hepatic steatosis. Diagnosis generally occurs soon after birth or in childhood. The case presented is significant for a delayed diagnosis of suspected BSS Type 1 which is rather uncommon in a developed country. Due to the detrimental complications of BSS, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, pancreatitis, and liver disease, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial. Pediatric providers must be knowledgeable about physical features of BSS and common presentations such as new onset diabetes, hypertriglyceridemia, or pancreatitis throughout early childhood and adolescence in order to avoid delayed diagnoses.
Related collections
Most cited references9

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
SEIPIN Regulates Lipid Droplet Expansion and Adipocyte Development by Modulating the Activity of Glycerol-3-phosphate Acyltransferase
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Diagnosis and treatment of lipodystrophy: a step-by-step approach

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found