- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fecal Microbiota and Metabolome of Children with Autism and Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified
Read this article at
Abstract
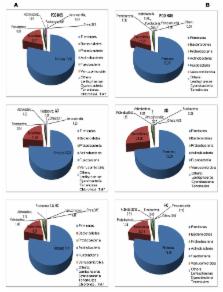
This study aimed at investigating the fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS) and autism (AD) in comparison to healthy children (HC). Bacterial tag-encoded FLX-titanium amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP) of the 16S rDNA and 16S rRNA analyses were carried out to determine total bacteria (16S rDNA) and metabolically active bacteria (16S rRNA), respectively. The main bacterial phyla (Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Fusobacteria and Verrucomicrobia) significantly ( P<0.05) changed among the three groups of children. As estimated by rarefaction, Chao and Shannon diversity index, the highest microbial diversity was found in AD children. Based on 16S-rRNA and culture-dependent data, Faecalibacterium and Ruminococcus were present at the highest level in fecal samples of PDD-NOS and HC children. Caloramator, Sarcina and Clostridium genera were the highest in AD children. Compared to HC, the composition of Lachnospiraceae family also differed in PDD-NOS and, especially, AD children. Except for Eubacterium siraeum, the lowest level of Eubacteriaceae was found on fecal samples of AD children. The level of Bacteroidetes genera and some Alistipes and Akkermansia species were almost the highest in PDD-NOS or AD children as well as almost all the identified Sutterellaceae and Enterobacteriaceae were the highest in AD. Compared to HC children, Bifidobacterium species decreased in AD. As shown by Canonical Discriminant Analysis of Principal Coordinates, the levels of free amino acids and volatile organic compounds of fecal samples were markedly affected in PDD-NOS and, especially, AD children. If the gut microbiota differences among AD and PDD-NOS and HC children are one of the concomitant causes or the consequence of autism, they may have implications regarding specific diagnostic test, and/or for treatment and prevention.
Related collections
Most cited references77
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found