- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Thoughts, perceptions and concerns of coastal residents regarding the discharge of tritium-containing treated water from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant into the Pacific Ocean
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
As a part of the decontamination process after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident of 2011, 1.32 million tonnes of tritium-containing water will be discharged from the power plant into the Pacific Ocean. Although radiobiological impacts of the treated water discharge on the public and the environment were reported to be minimal, Tomioka and Okuma locals expressed unease regarding the long-term recovery of their towns, which are economically dependent on the agricultural, fishery, and tourism sectors. This study presents thoughts, perceptions and concerns of Tomioka and Okuma locals regarding the discharge of FDNPP-treated water containing tritium into the Pacific Ocean to facilitate a more inclusive decision-making process that respects local stakeholder interests.
Methods
Conducted from November to December 2022, surveys were mailed to current residents and evacuees aged 20 years or older registered with the town councils.
Results
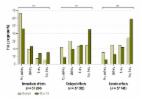
Out of 1268 included responses, 71.5% were from those > 65 years. 65.6% were unemployed, 76.2% routinely visited hospitals, and 85.5% did not live with children. 61% did not want to return to Okuma/Tomioka. Anxiety about radiation-related health effects (38.7%), consuming food produced in Okuma/Tomioka (48.0%) and genetic effects (45.3%) were low. >50% reported poor physical and mental health. 40% were acceptive, 31.4% were unsure, and 29.7% objected to the discharge plans. Multinomial regression analysis revealed that, compared to acceptive responders, those who objected were more likely to be female, unemployed, and have anxiety about radiation-related genetic effects and poor mental health. Unsure responders were similarly more likely to be female, anxious about radiation-related genetic effects and have poor mental health.
Conclusion
The poor mental health of the locals, connected to high levels of risk perception and anxiety about the loss of economic opportunities related to the discharge plans, must be addressed. The 30-year discharge process could handicap local industries and hamper post-disaster socioeconomic recovery due to the circulation of false rumours among consumers. These results highlight the need to actively involve residents in the towns’ recovery process to address local concerns. The focus should be on the judicious combination of transparent science with the human aspect of recovery and narratives highlighting dialogues between local stakeholders and experts to enable the locals and the general public to make informed decisions about their protection and future.
Related collections
Most cited references30

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Psychological distress and the perception of radiation risks: the Fukushima health management survey
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found