- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Primary intradural extramedullary Ewing sarcoma: A case report and literature review
Read this article at
Abstract
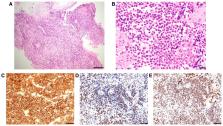
Tumors of the spinal cord and cauda equina show a wide spectrum of histology and require careful diagnosis and treatment. Primary intradural extramedullary Ewing sarcoma (IEES) is extremely rare, and initial imaging and clinical findings for this tumor mimic those of benign intradural spinal tumors. The present report describes a case of a 35-year-old woman who presented with IEES with meningeal seeding, and the literature on the management and clinical course of these tumors was reviewed. An examination revealed right-side leg dominant rapidly progressive hypoesthesia and motor deficits. MRI identified intradural tumors at the T12-L1 and L4-5 levels. Growth and an increase in the number of intradural tumors occurred over 3 weeks. Gadolinium-contrast T1-weighted MRI revealed diffusely enhanced signals for tumorous lesions with meningeal seeding in the cervical and thoracic spinal cord. Excision of a tumor at T12-L1 was performed to alleviate the symptoms and to make a histologic diagnosis. Microscopically, the tumor consisted of dense sheets of small round cells. Immunohistochemically, tumor cells showed intense and diffuse positive staining for CD99, ETS transcription factor ERG and Fli-1 proto-oncogene, ETS transcription factor (FLI1). The sequence analysis revealed the EWS RNA binding protein 1-FLI1 fusion transcript. The lesion was diagnosed as primary intradural ES. Adjuvant chemotherapy following radiotherapy for the whole spine was performed; however, multiple brain metastases were found at 10 months after diagnosis and the patient died of diffusely disseminated disease limited to the central nervous system without evidence of distant metastases at 16 months after the initial diagnosis. In a literature review of IEES cases, the 1- and 5-year overall survival rates were 79.8 and 26.6%, respectively, and the 1-, 2- and 5-year progression-free survival rates were 61.0, 52.3 and 10.9%, respectively. Therefore, primary IEES has a poor prognosis compared with ES of bone, and novel agents and treatment strategies are required.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ewing Sarcoma: Current Management and Future Approaches Through Collaboration.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical features and outcomes in patients with extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found