- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Read this article at
Abstract
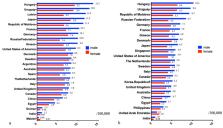
The number of new cases of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is increasing with a cumulative total of 495,773 cases worldwide, making it the fourteenth most common malignancy. However, it accounts for 466,003 deaths per year and is the seventh leading cause of cancer deaths. Regional differences in the number of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma appear to reflect differences in medical care, as well as racial differences. Compared to the prevalence of other organ cancers in Japan, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma ranks seventh based on the number of patients, eighth based on morbidity, and fourth based on the number of deaths, with a continuing increase in the mortality rate. Risk factors for developing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma include family history, genetic disorders, diabetes, chronic pancreatitis, and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. An issue that hinders improvement in the prognosis of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is the development of a strategy to identify patients with these risk factors to facilitate detection of the disease at a stage when intervention will improve survival.
Related collections
Most cited references67
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found